Study In japan a guide for international students
How does the idea of studying abroad sound to you? Exploring a new culture, different than yours, opens new paths in life you have never imagined. Studying abroad in Japan is an option you should seriously consider.
Japan or ‘’Nippon’’ ‘’Nihon’’ or as more widely called ‘’The Land of the Rising Sun’’ is an island country located in East Asia in the northwest of the Pacific Ocean. It consists of five main islands and spans in an around 7,000 island archipelago. Did you know that human habitation of the Japanese archipelago was traced back to prehistoric times, around 30,000 years ago?
Why study abroad in Japan? You will find yourself living in one of the most urbanized and densely populated countries in the world. In fact, the Greater Tokyo area is the most populous area in the world, with more than 37 million residents! In Japan, you will have the option to live in one of the main five islands: Hokkaido, Honshu, Shikoku, Kyushu or Okinawa.
About studying in Japan.

Japan is widely considered a safe country for students, with efficient public transportation. The country offers low-cost tuition and many professional opportunities. students than many other developed nations, lots of scholarship opportunities, low cost of living for students, generous part-time work allowances, ample graduate employment opportunities, and welcoming immigration system.
Student Visas To Japan

Foreigners planning to enter Japan must first acquire and be issued a visa. Residential status in Japan for foreign nationals entering the country under such visas is accorded according to the planned activities, status and position in Japan.
Residential status for university study, junior college study, technology colleges, professional training colleges or Japanese language schools in Japan is established as “Student.” The duration of stay is separately determined by the Minister of Justice for each applicant not more than 4 years and 3 months.
Japan Education System for Foreign Student.

Japanese education is governed by the Japan Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (MEXT). The policy today stands at one of lifelong learning, high-level professional education, and internationalization of tertiary education through measures such as the greater acceptance of foreign students, as the nation is undergoing a rapidly-deteriorating population shrinkage and aging.
Ranked among the most educated and productive countries of the world, Japan is a remarkable nation that flaunts a polished mix of rich culture and modern technology. A third-largest economy in the world, the Asian country has invested a considerable proportion of its GDP to improve education and boost research and development activity. Yet another thing that differentiates it from all the rest of the countries is Japan’s education system. From its age-based syllabus to giving importance to extracurricular development, Japan education system can be counted among the countries with the best education system in the world. Thus, in this blog, we shall inform you about various points related to the Japan school system as well as why it would be a wonderful idea to study in Japan.

We would like to hire skilled personnel regardless of nationality,” “We need personnel who can communicate in foreign languages and are also adapted to foreign situations,” “We would like to actively hire personnel with diverse backgrounds.” In Japan information technology, there are increasingly more companies operating based on these declarations, and the hiring of international students is increasing.
Japanese-Language Requirements to Study in Japan.

There’s no better way to learn Japanese than to study in Japan. Immersion in the language’s native environment accelerates learning, providing students with a deep understanding of both linguistic nuances and cultural contexts. Achieving proficiency in Japanese, such as a JLPT N2 or N1 level, opens doors to various opportunities, both in Japan and globally.
Age Requirements to Study in Japan 2024.
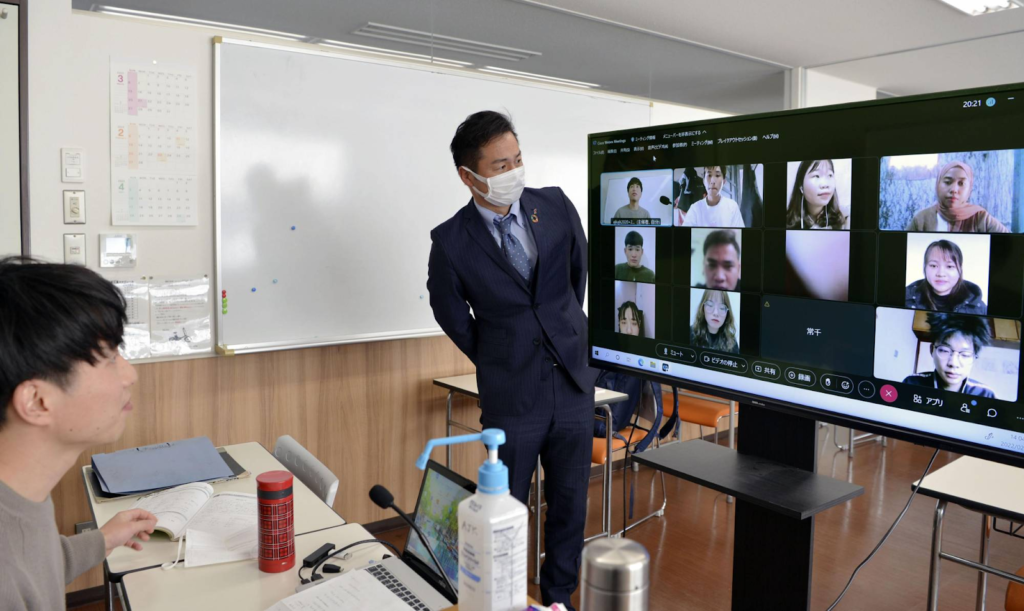

Most Japanese language schools require a high school diploma or its equivalent of 12 years of primary and secondary school education. Due to this, the candidates for student visas would normally need to be 18 years and older.
You can get a student visa at the Japanese Consulate of your native country by submitting a “Certificate of Eligibility for Resident Status” and “Certificate of Admission”.
Other than that, applying to study in Japan when you’re over 30 is very much the same as for anyone else. The slightly stricter requirements shouldn’t put anyone off, if it is something they want to pursue.
Being overseas when you are a bit older is actually very fulfilling. You have a different perspective on things than when you are in your late teens and early 20s. You may also have a clearer sense of what you want to do and where you want to go, as you will likely already have some work force experience and life experience. That will go a long way in keeping one motivated when the studying becomes difficult and all the kanji appear to be the same. Your work experience will also be to your advantage should you wish to work full-time in Japan. You can improve your language ability by two years of full-time study to business level. If you have the right qualifications, you’re highly likely to obtain a job that you wish.
Also, if you possess a Bachelor’s degree or have a very good business experience, a full-time programmer may be completed within one year and their excellent business network ensures you will receive the assistance you need in finding work after studies.
6 Steps to Study In Japan 2024.

1.Choosing a Japan Language school.
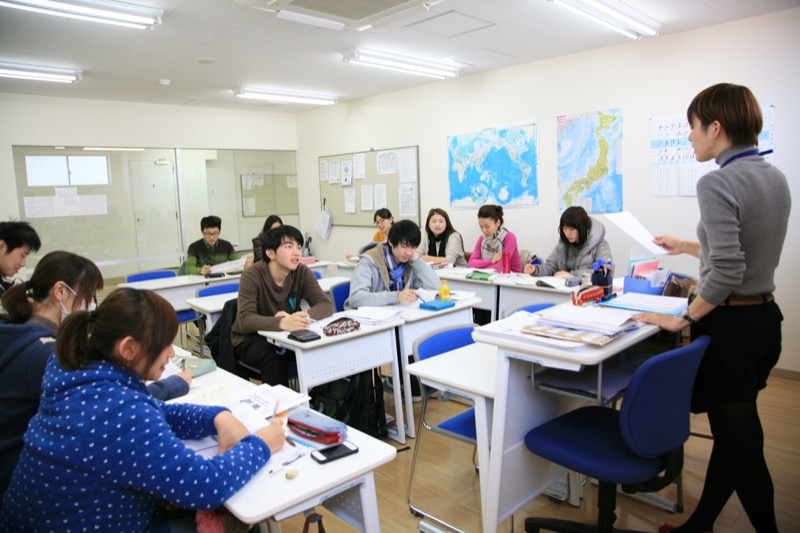

You can choose to study at a Japanese language school, a vocational school, a junior college, an undergraduate course, a master’s course or a doctoral course in Japan. Japanese language schools are places where you can start learning Japanese from the beginner level. There are courses only for Japanese learning. Completion of 13 years’ school education is essential for applying. Japan offers a variety of programs, from language schools to universities with specialized courses.
2. Do you want to study the Japanese language first, or go straight to a degree.

Usually international students first study Japanese at Japanese language institutes (for a period of six months to two years) and then advance to higher education. You get given a course so you can study and make progress, step by step, while being held accountable. There is a teacher that will help you correct your mistakes before you repeat them and learn the wrong things by accident.
3.Understand the application process.
Each school has its own application process, so make sure you understand what’s required for your chosen program.
Gather Necessary Documents: Typical documents include academic transcripts, recommendation letters, a personal statement, and proof of Japanese or English proficiency (depending on the language of instruction).
Application Deadlines: Mark the application deadlines on your calendar. Japanese schools often have different timelines compared to those in your home country.
4.Prepare all the documents needed for the COE after you receive your COE.

Certificate of Eligibility (在留資格認定証明書 hereafter “COE”), issued by the Ministry of Justice, Immigration Service Agency of Japan, certifies that you are the eligible person to enter Japan with certain Residence Status.
You need to have the COE for your visa application at the Embassy, Consulate-General of Japan in your country because they judge whether the applicant is appropriate to enter Japan or not.
Once you receive the COE, take it and the visa application form (obtained from the Japanese embassy in your country), photos and valid passport to the Japanese embassy or consulate in your city. The Embassy will issue you the actual student visa which can take anywhere from 3 – 7 days.
Tuition Fees & Scholarships

Tuition fees naturally vary based on the length of the course. The typical tuition is around 150,000 to 200,000 yen for a 3-month full-time program. In addition, most schools charge a registration fee of around 5,000 to 20,000 yen and an insurance fee of 10,000 yen per year in case of long-term programs.
In comparison to other popular study destinations like the US or the United Kingdom, tuition in Japan is quite reasonable for international students applying for Bachelor’s, Master’s and Doctorate degrees. For Bachelor’s studies, tuition in Japan fluctuates around 20-23,000 USD, for Master’s around 12,000 USD and for Doctorate studies around 5,000 USD per academic year.
An additional cost for every international student studying in Japan is the enrollment in the National Health Insurance (NHI). The National Health Insurance is essential as it reduces the medical costs in case of injury. You can register for the insurance in your closest local municipal office in Japan after you obtain your visa/residence permit.
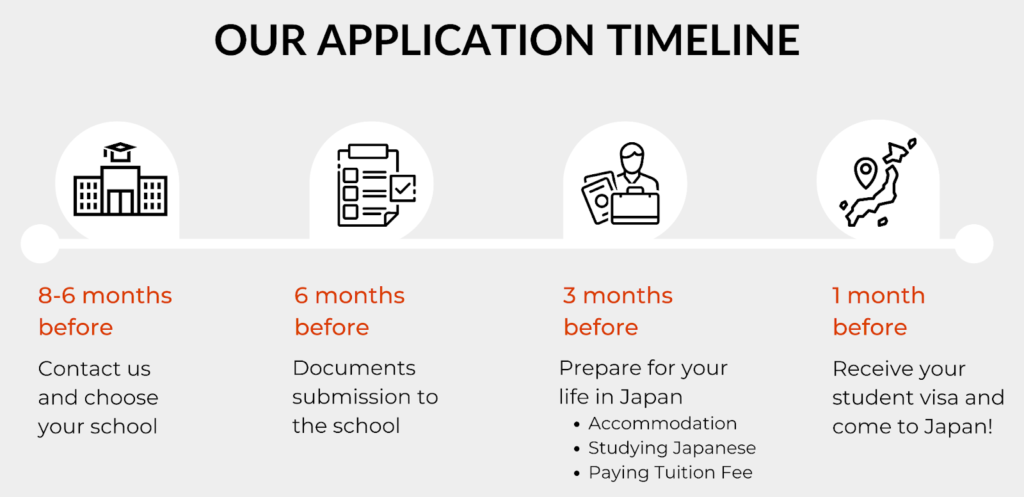
Application Timeline to Study In Japan 2023.
In addition to National scholarships, Japan has its own scholarship system to support the students. A program that supports current students who have excellent academic ability and are highly motivated to study.
Japanese language schools offer scholarships to students who excel academically (grades and attendance), are highly motivated to learn, and are role models for other students. Students may also be eligible for outside scholarships through the school’s recommendation.
All scholarships have requirements, so students who wish to apply should study carefully. If you have any questions, please contact us. Please note that the scholarship program is subject to change without notice.
Japan Language.

The 99.2% of people in Japan have Japanese as their first language. There are still a few lesser-spoken languages across the islands, including. The Japanese writing system combines Chinese characters, known as kanji (漢字, ‘Han characters’), with two unique syllabaries (or moraic scripts) derived by the Japanese from the more complex Chinese characters: hiragana (ひらがな or 平仮名, ‘simple characters’) and katakana (カタカナ or 片仮名, ‘partial characters’). Latin script (rōmaji ローマ字) is also used in a limited fashion (such as for imported acronyms) in Japanese writing. The numeral system uses mostly Arabic numerals, but also traditional Chinese numerals.
Japan Culture.

Japanese culture is described by the values of harmony, social conformity and consensus decision making. A major characteristic of Japanese people is their polite manners and punctuality.
When referring to facts about Japanese culture, multiple things come across our minds. From the cherry blossom trees opening the Sakura season every spring, the colorful classic kimono dresses, the alternative Harajuku Style and Japanese cosplay, to the famous national sport of Sumo wrestling, Karate, Judo, Jiu-Jitsu or calligraphy and origami, the list in unending!
The Japanese maintained its own unique identity and have given a lot to the contemporary world.
Housing & Living Costs.

Is it expensive to live in your own place in Japan? Should you choose the dormitory instead of a rented room? Let’s see.
Monthly expenses vary widely with lifestyle and location. A budget of around $1500 to $2000 can cover basic living costs in many areas. Living in Japan, particularly for students, can cost around 88,330 yen per month, including Housing rent, meals, mobile phone, and health insurance.
If you decide to find a place to rent, you will easily find one for any budget. There are rooms near the university starting from 15,000 yen a month. The room would be rather small, and you will have to pay for the utilities, but it would be your own separate room. Larger flats are available for 30,000~40,000 yen a month.
